Overview
Tasketch is an desktop application designed for busy NUS students who have many tasks, assignments and deadlines everyday. Tasketch helps you to manage your everyday time by giving you an overview of all the time planned for all the tasks in a daily manner.Tasketch uses minimal (GUI) elements, instead opting for a faster Command Line Interface (CLI) while maintaining the benefits of the GUI. So, if you are used to the command line, Tasketch is sure to help manage your time effectively.
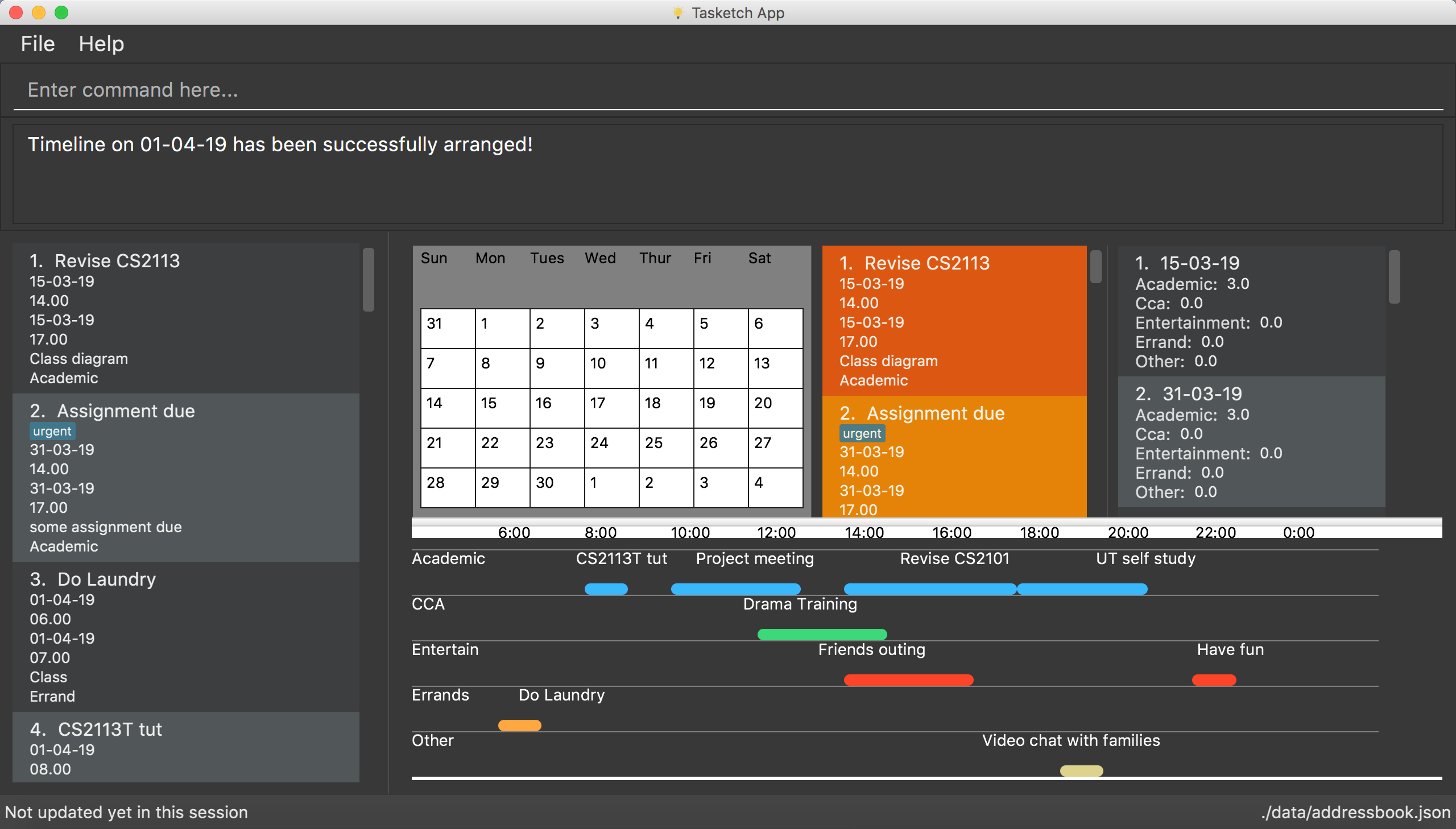
Figure 1. An overview of our application.
Summary of contributions
-
Major enhancement 1: Added login feature.
-
What it does: It allows the user to log into the Tasketch with their account. If the user doesn’t login, all commands will be locked up except
-
login
-
loginstatus
-
listaccounts
-
findaccount
-
help
-
history
-
exit After logging in, all commands will be unlocked for user. Besides, the user can add new accounts, edit accounts information, check login status, list all accounts, find accounts containing keywords, and delete accounts.
-
-
Justification: This feature prevent Tasketch from unauthorized modification. A user cannot modify the content of Tasketch without logging in.
-
Highlights: Tasketch provides a default account whose username and password are both "admin". We suggest that do not delete that account.
-
-
Major enhancement 2: Added Auto-complete feature.
-
What it does: If you type something wrongly, the app will automatically correct type error and fulfill their incomplete typed command in command line. If you type correct command, then it can help fulfill the format string of the parameter for corresponding command.
-
Justification: This feature improves the product significantly because a user may not be familiar with the command and may be hard to type a very long string of parameters
-
Highlights: This enhancement will be affected by existing commands and commands to be added in future. It required an in-depth analysis of design alternatives. The implementation too was challenging as if user type a command wrongly it required an algorism that can compute the similarity compared with the command user type in and existing command and return the most similar command. **Credits: I apply a math concept of "Edit distance", which means caculate the similarity between two strings by caculating the time of editing for converting one string to another string.
-
-
Minor enhancement:
-
Implement 'edit' command that allows the user to edit his task information
-
-
Code contributed: [Functional code] [Test code] {give links to collated code files}
-
Other contributions
-
Project management:
-
Brainstorm new features for Tasketch
-
-
Enhancements to existing features:
-
Fix bugs for and Update previous commands.
-
Updated the Import and Export command. Makes Tasketch can import and export account list as a Json file(Pull requests #160).
-
-
Documentation:
-
Update User Guide and Developer Guide. (available UserGuide, DeveloperGuide)
-
-
Community:
-
Reported bugs and offered suggestions for other teams in the class
-
PRs reviewed (with non-trivial review comments)
-
-
Contributions to the User Guide
Given below are sections I contributed to the User Guide. They showcase my ability to write documentation targeting end-users. |
Quick Start
-
Before start to use Tasketch. You should first log into this app via login command. For example:
-
login u/admin p/admin
-
-
Tasketch provides a default account whose username and password are both "admin". We suggest that do not delete that account.
-
If you do not login, you can only execute following commands and other commands are locked.
-
login
-
loginstatus
-
listaccounts
-
findaccount
-
help
-
history
-
exit
-
Login
Login
You must login to manage your Tasketch and unlock all commands.
Format: login u/USERNAME p/PASSWORD
Examples:
-
login u/admin p/admin
login with the default account if no account has logged in Tasketch.
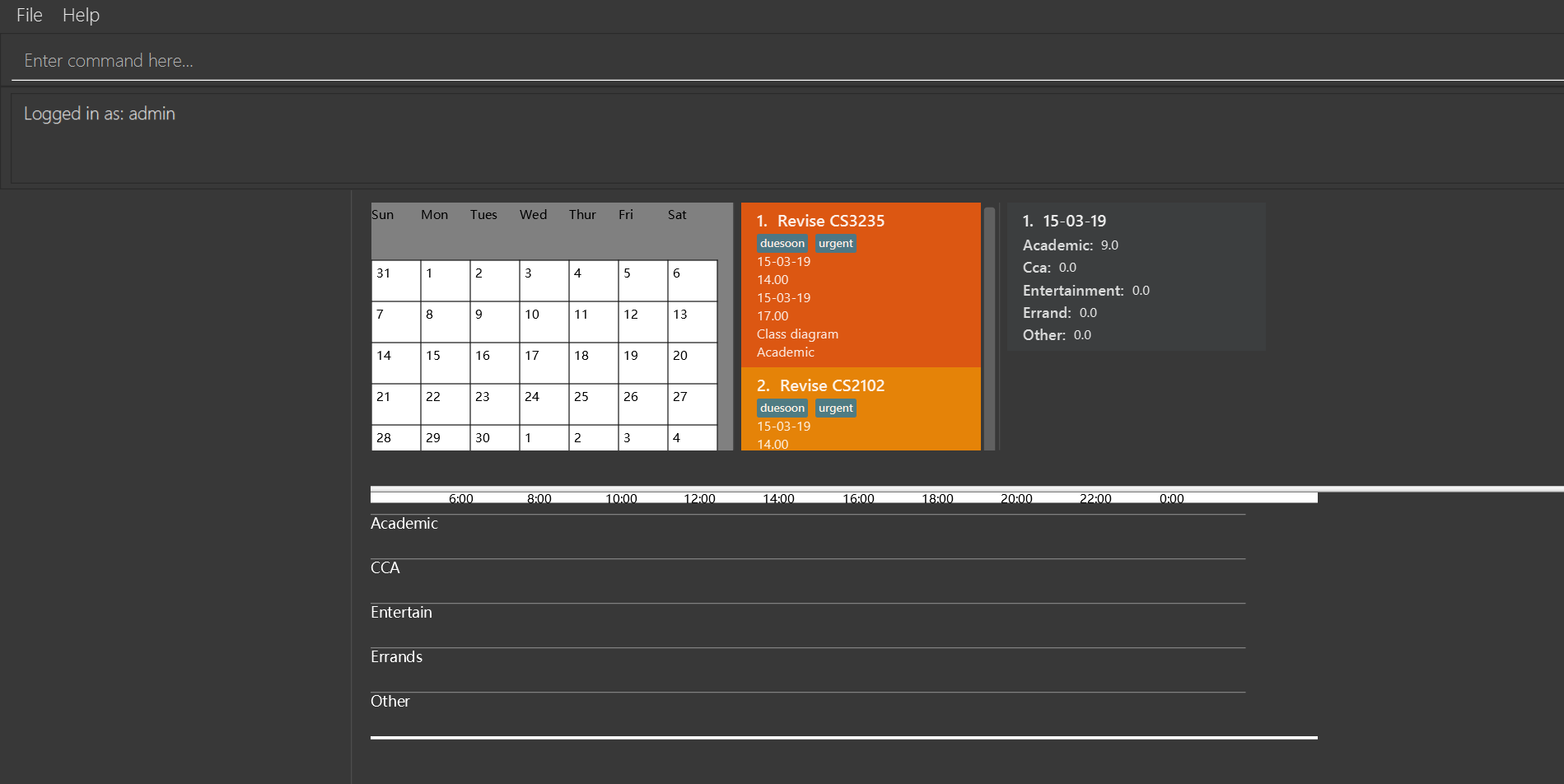
-
login u/admin p/admin
login with the default account if an account has already logged in Tasketch..
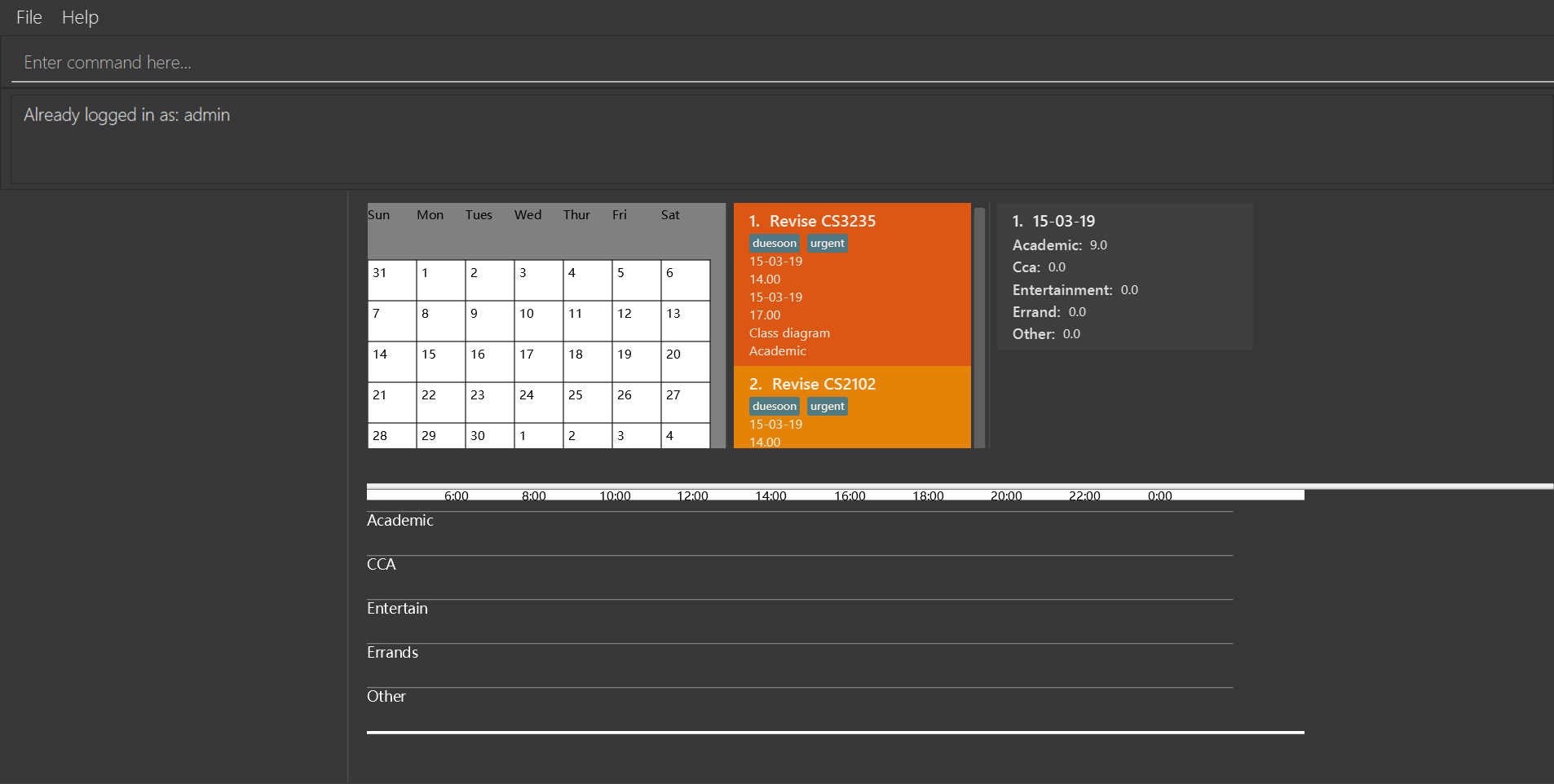
LoginStatus
Shows whether the user log in Tasketch and which account the user logged in.
Format: loginstatus
Examples:
-
loginstatus
If you do not login with any accounts, returnNot logged in.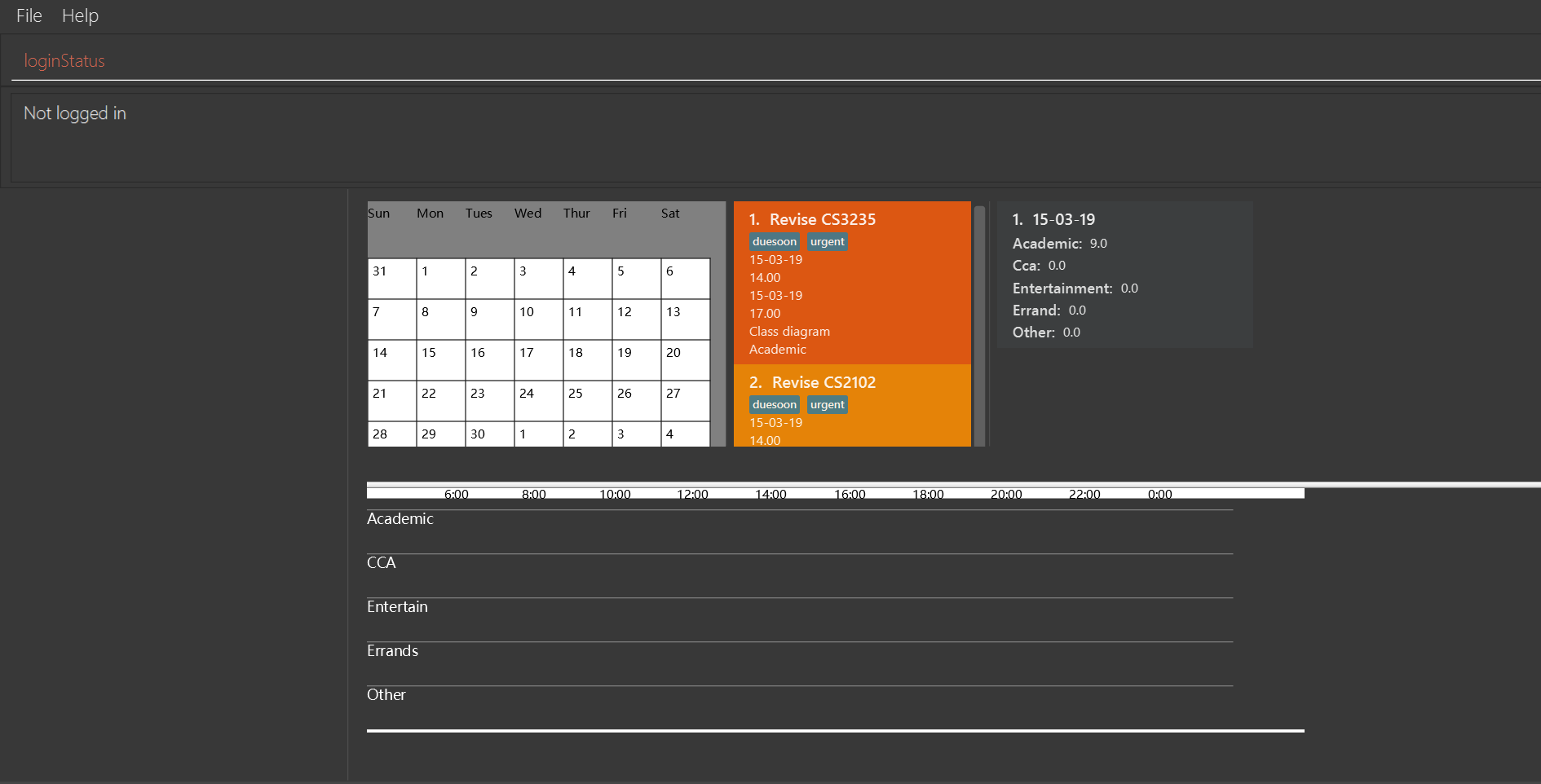
-
loginstatus
If you login with default account, returnLogged in as: admin.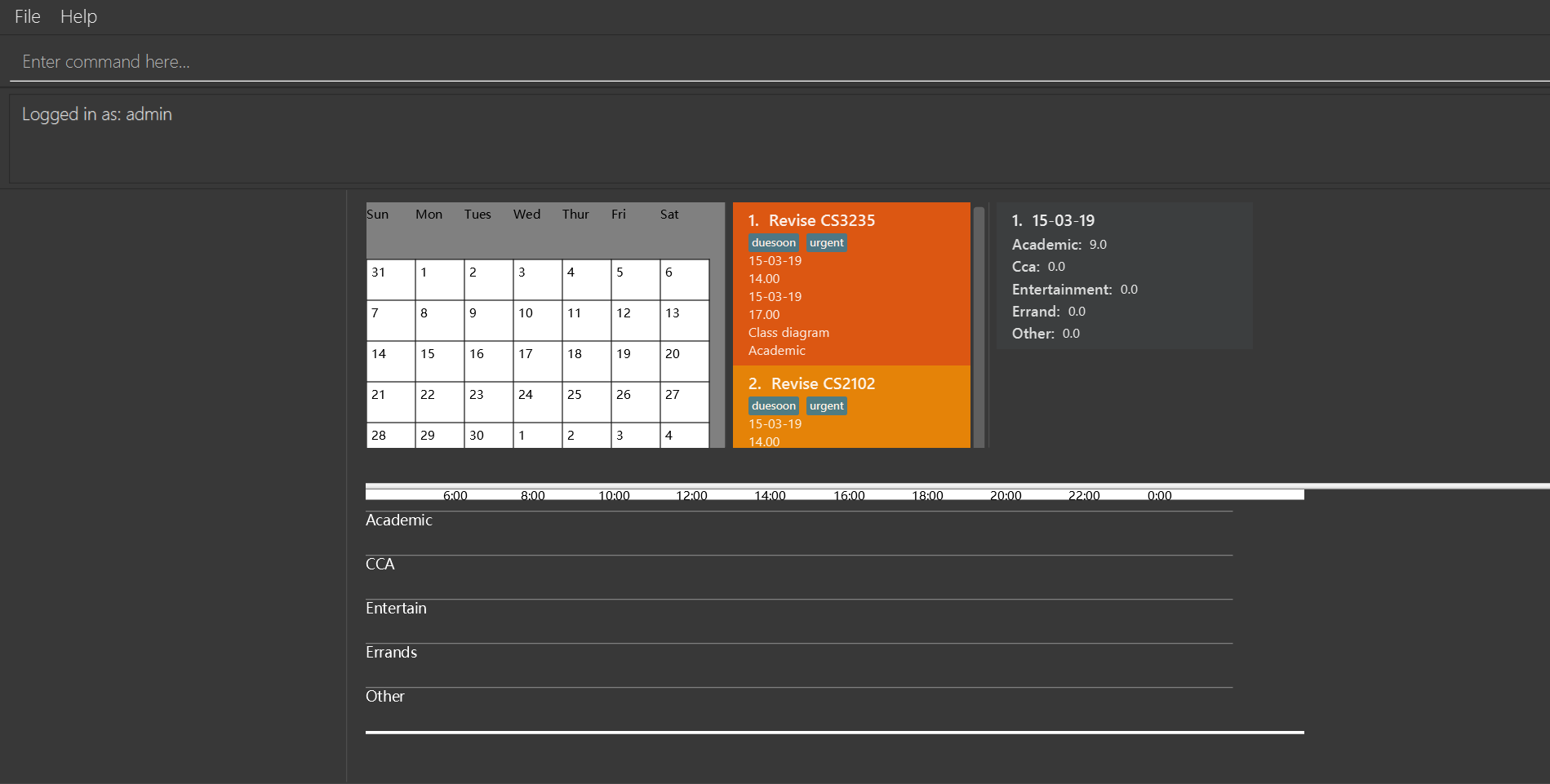
Logout
Log out if you have logged in with an account.
Format: logout
Examples:
-
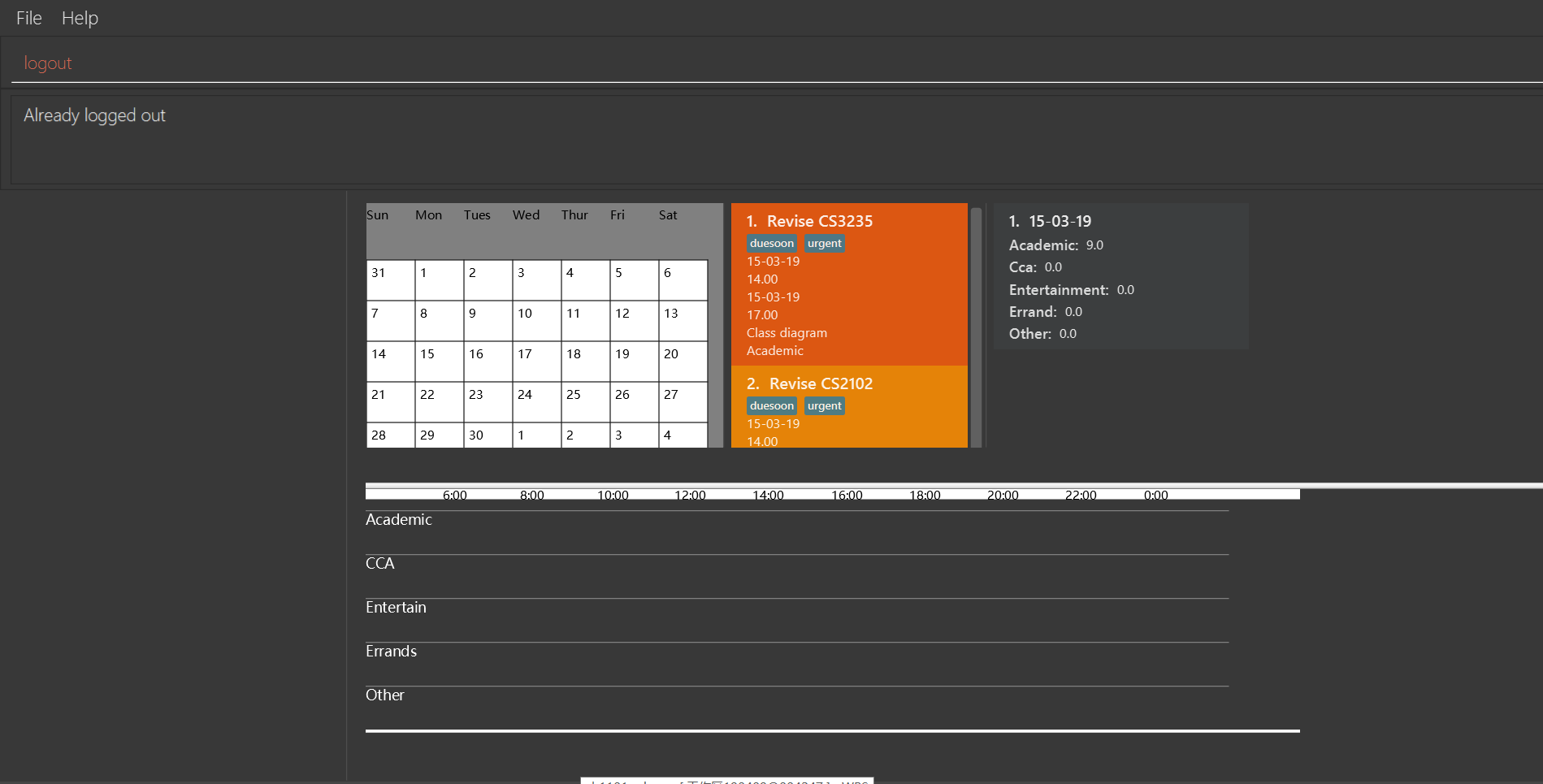
logout
If you do not login with any accounts, returnAlready logged out.
-
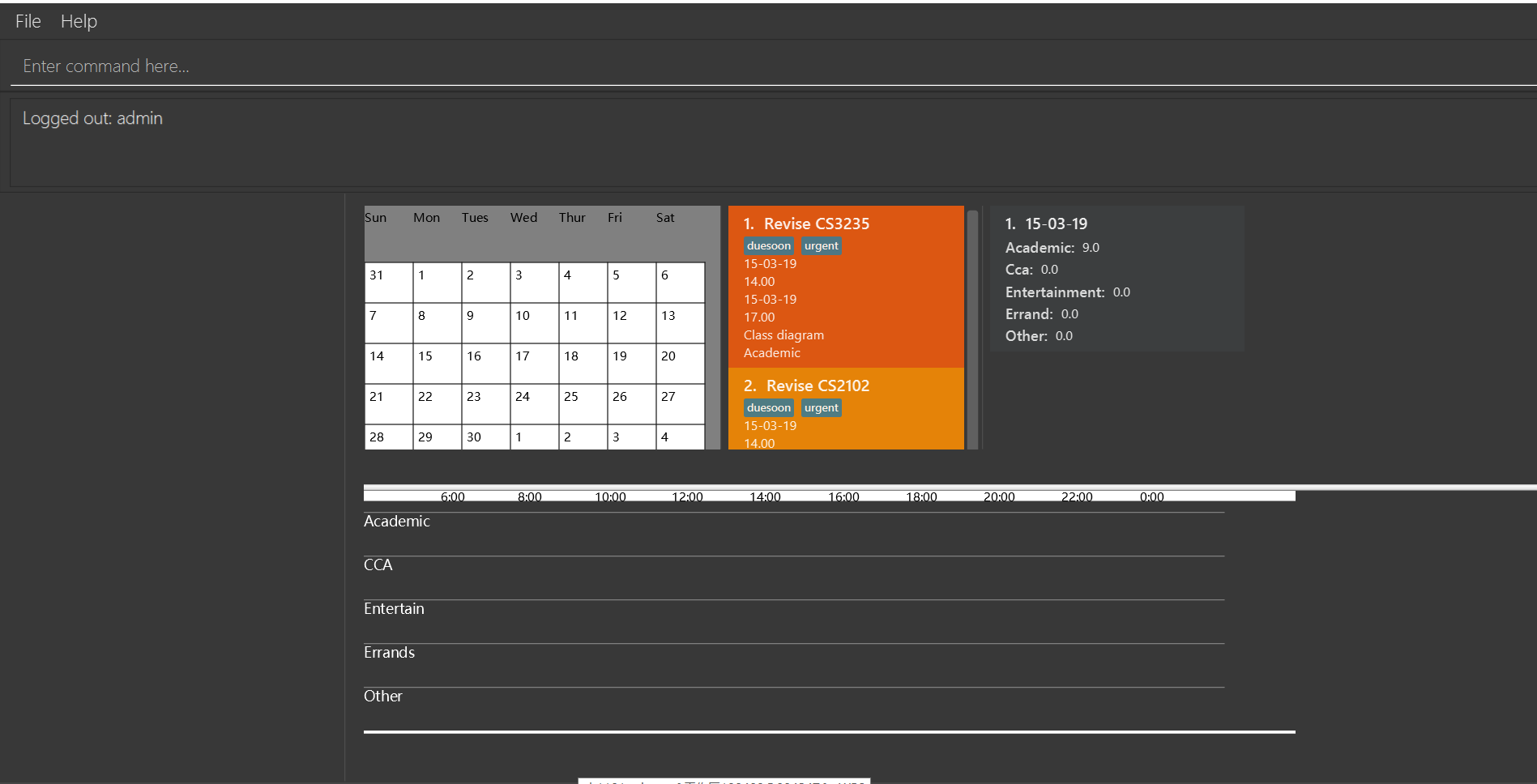
logout
If you login with default account, returnLogged out: admin.
Automatically complete input command for user
If you type something wrongly, the app will automatically correct type error and fulfill their incomplete typed command in command line.
Examples:
-
If you want to type
list, you can typeliinstead, and pressTABon keyboard. The system will automatically fulfill the command in command line withlist. -
If you want to type
history, but you typehistoeinstead, and presstapon keyboard. The system will automatically fulfill the command line withhistory. -
If you want to type
add, but you typeaefwinstead, and presstapon keyboard. The system will automatically fulfill the command line withNo command matched.
Contributions to the Developer Guide
Given below are sections I contributed to the Developer Guide. They showcase my ability to write technical documentation and the technical depth of my contributions to the project. |
Login feature
The login feature will unlock all commands for the users, otherwise the user can only execute following commands:
-
login -
loginStatus -
listAccounts -
findAccount -
help -
history -
exist
Current Implementation
The login mechanism is facilitated by LoginCommand. It extends Command and implements the following operations:
-
LoginCommand#modifyLoginStatus()— checks whether there exists such username and corresponding password in accountlist. If troue, updates the logged in account status in Model accordingly. -
LoginCommand#execute()— calls LoginCommand#modifyLoginStatus(). Then, checks login status in Model and displays a login success message if true and displays a failure message otherwise.
These operations are exposed in the Model interface as Model#setLoggedInUser() and Model#getLoginStatus() respectively.
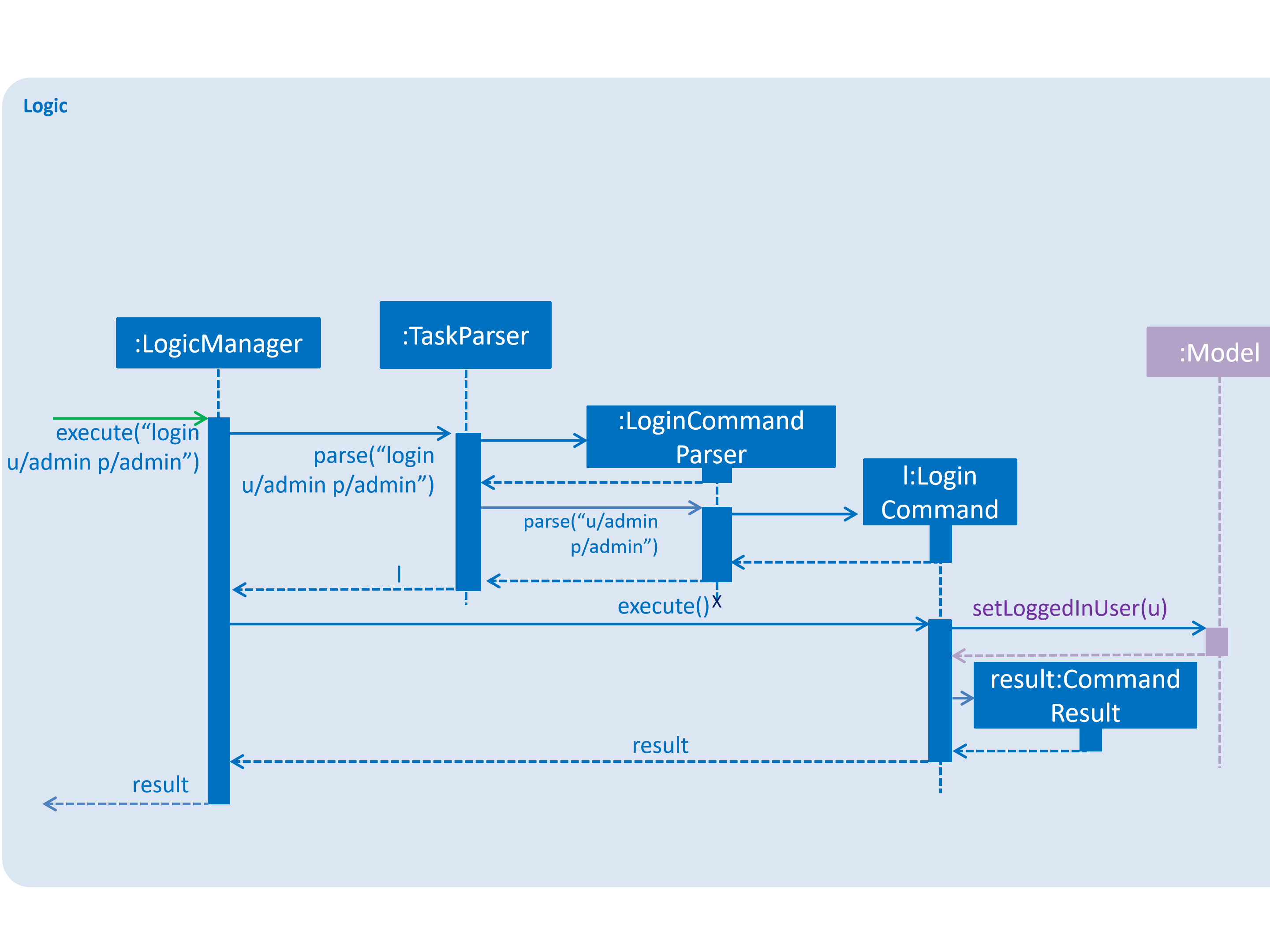
Given below is an example usage scenario and how the LoginCommand mechanism behaves at each step.
Step 1: The user executes login u/admin p/admin command to log into Tasketch. The username and admin are both "admin".
Step 2: The execute command calls Model#getLoginStatus() and checks whether the user has already logged in with an account. If true, execute throws a CommandException notifying the user that he is already logged in.
Step 3: The execute command then calls LoginCommand#modifyLoginStatus().It checks whether the username "admin" and its corresponding password "admin" exists in the accountlist.
Step 4: If there exists such an account, LoginCommand#modifyLoginStatus() calls Model#setLoggedInUser() which updates the logged in account status in model with the logged in account set to admin and logged in status set to true.
Step 5: The login command checks the login status according to Model#getLoginStatus(). A success message is printed if true; otherwise a failure message is printed.
The following sequence diagram shows how the login operation works:
Design Considerations
Aspect: How login executes
-
Alternative 1 (current choice): Check against various accounts stored in a file and allow access if match.
-
Pros: It allows multiple accounts to access to Taskbook.
-
Cons: It may cost more memory to store the account list.
-
-
Alternative 2: Checks against a single account that can be modified.
-
Pros: It will use less memory.
-
Cons: Only one account can access to Taskbook. If the user accidently loses the account, the whole application may be locked up.
-
Automatically complete input command feature
Auto-complete uses tab as a signal to trigger auto-complete and the command box will automatically complete the incomplete input.
Current Implementation
When a user press TAB key, if the command is incomplete, Auto-complete feature will fulfill the automatically. If the command is completed, Auto- complete feature will fulfill the format string of corresponding parameters of the command.
Given below is an example usage of how the WrongCommandSuggestion behaves at each step.
Step 1: The user type an command in command line and press TAB from keyboard.
Step 2: The command will be compared with CommandBox#CommandList. If the typed command is in CommandBox#CommandList, which means it is a valid command, then call CommandBox#showParameterForCommand() to fulfill the format string of parameters of the command.
Step 3: Otherwise, TAB will call CommandBox#autoCompleteInputCommand() to fulfill the incomplete command.
Step 4: CommandBox#autoCompleteInputCommand() will call CommandBox#getMostSimilarCommand() to get the most similar command from Comm,andBox#CommandList.
Step 4: CommandBox#getMostSimilarCommand() will call CommandBox#compare() to get the similarity by caculating the times of editing needed for changing the input command into command in CommandBox#CommandList.
Step 5: If the similarity between the input command and the most similar command is more than 0.5, then replace the incomplete command with the most similar command. Otherwise, fulfill the command line with "No matched command".
The following sequence diagram shows an example of how the Auto-complete operation works with incomplete command histoe (closest command is history):
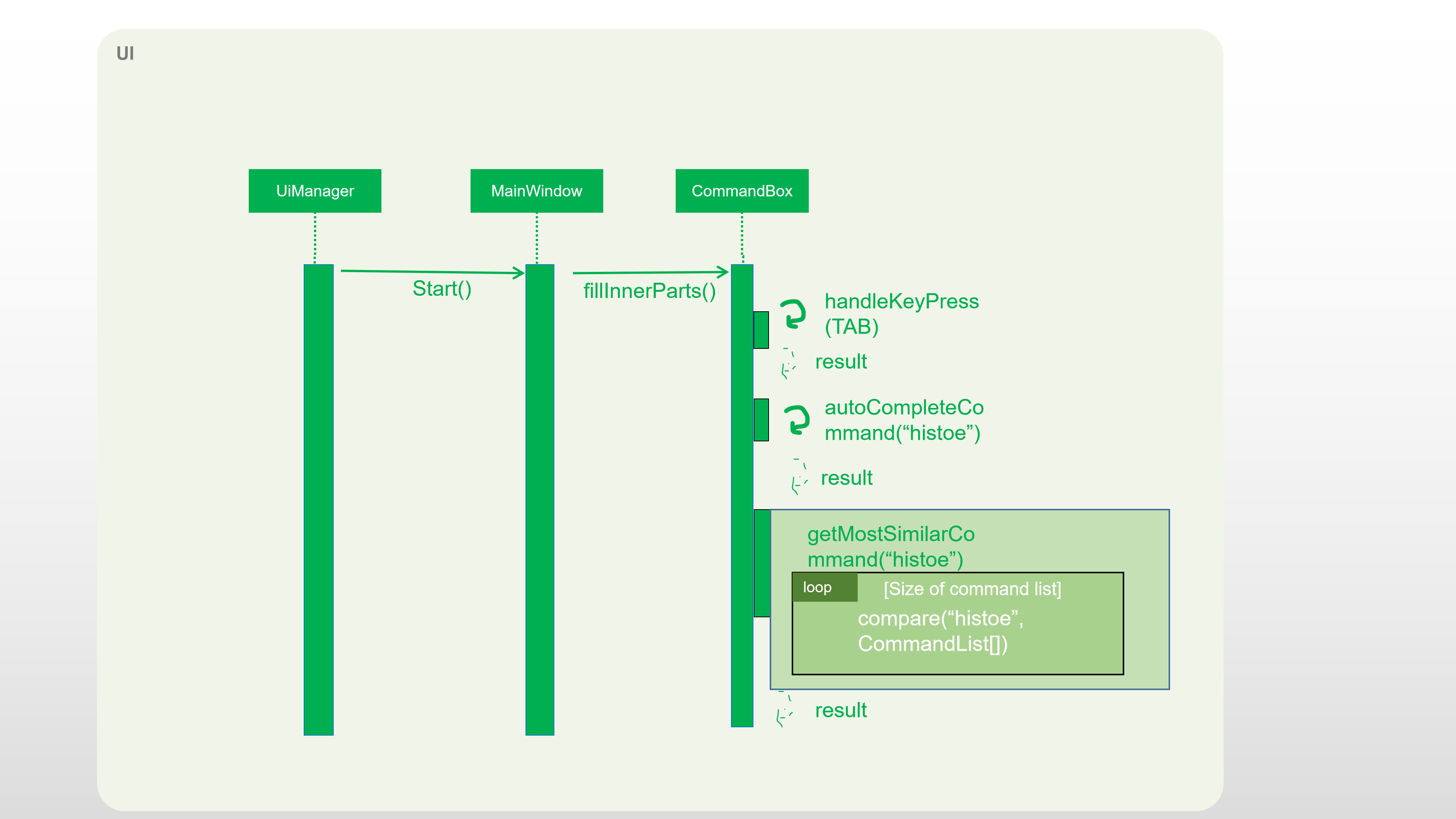
Design Considerations
-
Alternative 1: Auto-complete the input command by that if the input incomplete command is a substring of a command in CommandList, fulfill the input command with that command.
-
Pros: Simple.
-
Cons: If the user wrongly types the incomplete command, it can not correct them.
-
-
Alternative 2(current choice):if the input incomplete command is a substring of a command in CommandList, fulfill the input command with that command. If the input incomplete command is not a substring of any commands in CommandList, caculate the similarity and return the most similar command by applying a math concept: Levenshtein Distance.
-
Pros: Even if the user wrongly type a command, Auto-complete feature can correct it.
-
Cons: Difficult to design the algorithm.
-
PROJECT: PowerPointLabs
{Optionally, you may include other projects in your portfolio.}